October 21, 2012 - By Bruce Goldman
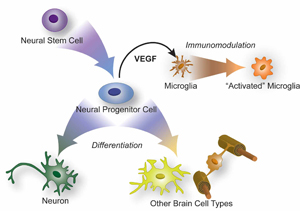
Rapidly dividing daughter neural progenitor cells, the progeny of neural stem cells, can differentiate into most types of cells that inhabit the brain. But they also secrete substances that stimulate the brain's resident immune cells, or microglla, Tony Wyss-Coray's group has found.
The brain’s key “breeder” cells, it turns out, do more than that. They secrete substances that boost the numbers and strength of critical brain-based immune cells believed to play a vital role in brain health. This finding adds a new dimension to our understanding of how resident stem cells and stem cell transplants may improve brain function.
Many researchers believe that these cells may be able to regenerate damaged brain tissue by integrating into circuits that have been eroded by neurodegenerative disease or destroyed by injury. But new findings by scientists at the Stanford University School of Medicine suggest that another process, which has not been fully appreciated, could be a part of the equation as well. The findings appear in a study published online Oct. 21 in Nature Neuroscience.
“Transplanting neural stem cells into experimental animals’ brains shows signs of being able to speed recovery from stroke and possibly neurodegenerative disease as well,” said Tony Wyss-Coray, PhD, professor of neurology and neurological sciences in the medical school and senior research scientist at the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System. “Why this technique works is far from clear, though, because actually neural stem cells don’t engraft well.”
Neural stem cells can endure essentially unchanged for decades in two places in the mammalian brain, replicating just enough to meet the routine needs of those regions. In most parts of the brain, they aren’t found at all.
While of critical importance to maintaining healthy brain function, true neural stem cells are rare. Far more common are their immediate progeny, which are called neural progenitor cells, or NPCs. These robust, rapidly dividing cells are poised to travel down a committed path of differentiation to yield new brain cells of several different types including neurons.
It’s known that treating humans with radiation or drugs that prevent NPC replication causes memory deficits (“chemo brain”) and, in children, IQ losses of up to 20 points. Conversely, studies are being initiated to see whether infusing neural stem cells into brains affected by Alzheimer’s disease can enhance patients’ memory function.
One category of brain cells, microglia, descends not from neural stem cells but from an immune lineage and retains several features of immune cells. “Microglia are the brain’s own resident immune cells,” Wyss-Coray said. Unlike most other mature brain cells, microglia can proliferate throughout adulthood, especially in response to brain injury. They can, moreover, migrate toward injury sites, secrete various “chemical signaling” substances, and gobble up bits of debris, microbial invaders or entire dead or dying neurons.

Tony Wyss-Coray
Microglia normally are distributed throughout the brain — rather small, quiescent cells sprouting long, skinny projections that meekly but efficiently survey large areas that, taken together, cover the entire brain. But if this surveillance reveals signs of a disturbance, such as injury or infection, the microglia whirl into action. They begin proliferating and their puny bodies puff up, metamorphosing from mild-mannered Clark Kent-like reporters to buffed Supermen who fly to the scene of trouble, where they secrete substances that can throttle bad actors or call in reinforcements. Within these activated cells, internal garbage disposals called lysosomes form in large numbers and start whirring, ready to make mincemeat out of pathogens or cellular debris.
In addition to their part patrol-officer, part cleanup-crew status, microglia can also secrete substances that help neurons thrive. They also contribute to the ongoing pruning of unneeded connections between neurons that occurs throughout our lives.
But like immune cells elsewhere, said Wyss-Coray, microglia can be a force for evil if they engage in too much or inappropriate activity. They might, for instance, start to remove healthy cells (as occurs in Parkinson’s) or stop cleaning up garbage strewn about the brain (for example, Alzheimer’s plaque).
In a series of experiments, Wyss-Coray and his colleagues have shown that NPCs secrete substances that activate microglia. First, the researchers observed that microglia were uncharacteristically abundant and activated in the two regions in the mammalian brain where NPCs reside and new neurons are formed. Wondering whether the NPCs might be causing this increased microglial activity, the investigators incubated mouse microglia in a culture medium in which NPCs had previously been steeped. Two days later, they saw that the microglia had multiplied more, expressed different amounts of various signal molecules and featured more lysosomes. “The microglia were ready for action,” said Wyss-Coray.
So they injected NPCs into an area of mice’s brains where these cells are normally not found. In the same area in the opposing brain hemisphere, they injected a control solution. Again they found significant differences in microglial proliferation and activity, and more microglia in the NPC-injected side had assumed a “Superman” as opposed to a “Clark Kent” body shape. When they repeated this experiment using only the NPCs’ “discarded bath water” rather than NPCs themselves, they got similar results.
Clearly NPCs were secreting something, or some things, that were spurring microglia to action.
Using sophisticated lab techniques, the team monitored purified NPCs plus several other cell types found in the brain and assessed nearly 60 different substances known to have powerful cell-to-cell signaling properties. Several such substances, it turned out, were secreted in much larger amounts by NPCs than by the other cell types: most notably, vascular endothelial growth factor, or VEGF — a well-known molecule produced by many cell types throughout the body. VEGF stimulates the formation of blood vessels and exerts a beneficial effect on neurons. Conversely, drugs that block VEGF (such as Avastin) are frequently used to combat cancer because tumors require an immense blood supply in order to grow quickly.
VEGF is also known to boost microglial proliferation. Because it is produced in such volumes by NPCs, Wyss-Coray’s team wanted to see if VEGF alone could mimic any of the changes wrought by NPCs or their culture-medium-borne detritus. So they injected VEGF into mice’s right brain hemisphere, and saline solution into the left — again with the same outcomes. Taking the opposite tack, the team injected NPC-saturated medium devoid of the cells, as they had done earlier. But this time they first used various laboratory techniques to deplete the fluid of the VEGF secreted by its former inhabitants. Doing this almost completely reversed its microglia-activating effects.
“All of this strongly suggests that VEGF produced by NPCs is playing a strong role in influencing microglial behavior,” said Wyss-Coray. “This is important, because in all neurodegenerative diseases we know of we see microglia out of control.” The new finding may open the door to reprogramming misbehaving microglia to play better with other cells.
The study’s first author was graduate student Kira Mosher. Other contributors were graduate student Gregor Bieri; postdoctoral scholars Robert Andres, MD, Takeshi Fukuhara PhD, Maiko Hasegawa-Moriyama MD, PhD, and Yingbo He, PhD; and Raphael Guzman, MD, a former associate professor of neurosurgery now at the University of Basel, Switzerland. The work was funded by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine and the National Institute on Aging.
Information about the medical school’s Department of Neurology and Neurological Sciences, which also supported the work, is available at http://neurology.stanford.edu/.
About Stanford Medicine
Stanford Medicine is an integrated academic health system comprising the Stanford School of Medicine and adult and pediatric health care delivery systems. Together, they harness the full potential of biomedicine through collaborative research, education and clinical care for patients. For more information, please visit med.stanford.edu.